Page 30 - BEc_Handbook_2024_2025
P. 30
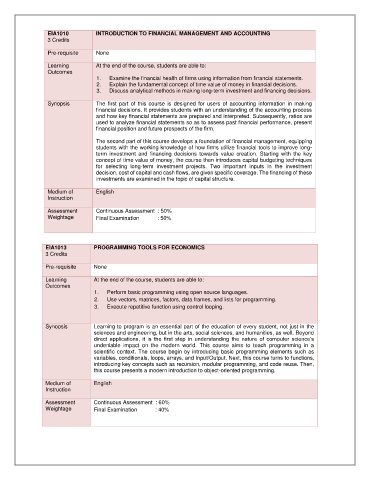
EIA1010 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND ACCOUNTING
3 Credits
Pre-requisite None
Learning At the end of the course, students are able to:
Outcomes
1. Examine the financial health of firms using information from financial statements.
2. Explain the fundamental concept of time value of money in financial decisions.
3. Discuss analytical methods in making long-term investment and financing decisions.
Synopsis The first part of this course is designed for users of accounting information in making
financial decisions. It provides students with an understanding of the accounting process
and how key financial statements are prepared and interpreted. Subsequently, ratios are
used to analyze financial statements so as to assess past financial performance, present
financial position and future prospects of the firm.
The second part of this course develops a foundation of financial management, equipping
students with the working knowledge of how firms utilize financial tools to improve long-
term investment and financing decisions towards value creation. Starting with the key
concept of time value of money, the course then introduces capital budgeting techniques
for selecting long-term investment projects. Two important inputs in the investment
decision, cost of capital and cash flows, are given specific coverage. The financing of these
investments are examined in the topic of capital structure.
Medium of English
Instruction
Assessment Continuous Assessment : 50%
Weightage Final Examination : 50%
EIA1013 PROGRAMMING TOOLS FOR ECONOMICS
3 Credits
Pre-requisite None
Learning At the end of the course, students are able to:
Outcomes
1. Perform basic programming using open source languages.
2. Use vectors, matrices, factors, data frames, and lists for programming.
3. Execute repetitive function using control looping.
Synopsis Learning to program is an essential part of the education of every student, not just in the
sciences and engineering, but in the arts, social sciences, and humanities, as well. Beyond
direct applications, it is the first step in understanding the nature of computer science’s
undeniable impact on the modern world. This course aims to teach programming in a
scientific context. The course begin by introducing basic programming elements such as
variables, conditionals, loops, arrays, and Input/Output. Next, this course turns to functions,
introducing key concepts such as recursion, modular programming, and code reuse. Then,
this course presents a modern introduction to object-oriented programming.
Medium of English
Instruction
Assessment Continuous Assessment : 60%
Weightage Final Examination : 40%