Page 41 - ASEAN-EU Dialogue 2018: Regional and Inter-Regional Economic Cooperation: Identifying Priorities for ASEAN and the EU
P. 41
1.26
16,000
1.13 13,972 1.2
1.07
Expenditure (RM million) 12,000 0.63 0.64 0.79 20.9% 10,613 26.5% 1.0 GERD/GDP (%)
14,000
10,000
0.8
8,511
19.3%
8,000
6,071
6,000
0.4
3,647 15.4% 0.6
4,000 2,844
9.6% 0.2
2,000 22.8%
77.2% 90.4% 84.6% 79.1% 80.7% 73.5%
0 0.0
2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014
Year
Current Expenditure Capital Expenditure Total GERD/GDP (%)
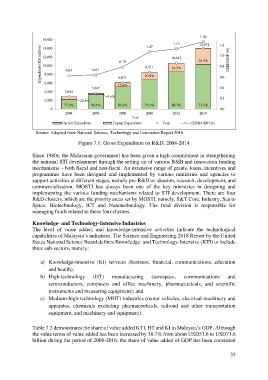
Source: Adopted from National Science, Technology and Innovation Report 2016
Figure 7.1: Gross Expenditure on R&D, 2004-2014
Since 1980s, the Malaysian government has been given a high commitment in strengthening
the national STI development through the setting up of various R&D and innovation funding
mechanisms – both fiscal and non-fiscal. An extensive range of grants, loans, incentives and
programmes have been designed and implemented by various ministries and agencies to
support activities at different stages, namely pre-R&D or ideation, research, development, and
commercialisation. MOSTI has always been one of the key ministries in designing and
implementing the various funding mechanisms related to STI development. There are four
R&D clusters, which are the priority areas set by MOSTI, namely, S&T Core, Industry, Sea to
Space, Biotechnology, ICT and Nanotechnology. The fund division is responsible for
managing funds related to these four clusters.
Knowledge- and Technology-Intensive Industries
The level of value added, and knowledge-intensive activities indicate the technological
capabilities of Malaysia’s industries. The Science and Engineering 2018 Report by the United
States National Science Board defines Knowledge- and Technology-Intensive (KTI) to include
three sub-sectors, namely:
a) Knowledge-intensive (KI) services (business, financial, communications, education
and health),
b) High-technology (HT) manufacturing (aerospace, communications and
semiconductors, computers and office machinery, pharmaceuticals, and scientific
instruments and measuring equipment); and
c) Medium-high-technology (MHT) industries (motor vehicles, electrical machinery and
apparatus, chemicals excluding pharmaceuticals, railroad and other transportation
equipment, and machinery and equipment).
Table 7.2 demonstrates the share of value added KTI, HT and KI in Malaysia’s GDP. Although
the value terms of value added has been increased by 38.7% from about USD51.6 to USD71.6
billion during the period of 2008-2016, the share of value added of GDP has been consistent
35