Page 65 - AEI Insights 2019 - Vol. 5, Issue 1
P. 65
Ziegenhain, 2019
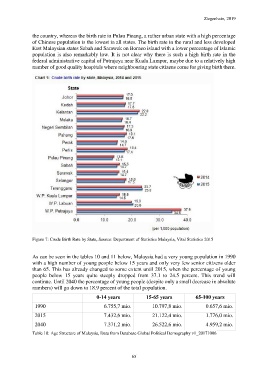
the country, whereas the birth rate in Pulau Pinang, a rather urban state with a high percentage
of Chinese population is the lowest in all states. The birth rate in the rural and less developed
East Malaysian states Sabah and Sarawak on Borneo island with a lower percentage of Islamic
population is also remarkably low. It is not clear why there is such a high birth rate in the
federal administrative capital of Putrajaya near Kuala Lumpur, maybe due to a relatively high
number of good quality hospitals where neighbouring state citizens come for giving birth there.
Figure 7: Crude Birth Rate by State, Source: Department of Statistics Malaysia, Vital Statistics 2015
As can be seen in the tables 10 and 11 below, Malaysia had a very young population in 1990
with a high number of young people below 15 years and only very few senior citizens older
than 65. This has already changed to some extent until 2015, when the percentage of young
people below 15 years quite steeply dropped from 37.1 to 24.5 percent. This trend will
continue. Until 2040 the percentage of young people (despite only a small decrease in absolute
numbers) will go down to 18.9 percent of the total population.
0-14 years 15-65 years 65-100 years
1990 6.755,7 mio. 10.797,8 mio. 0.657,6 mio.
2015 7.432,6 mio. 21.122,4 mio. 1.776,0 mio.
2040 7.371,2 mio. 26.522,6 mio. 4.959,2 mio.
Table 10: Age Structure of Malaysia, Data from Database Global Political Demography v1_20171006
65