Page 155 -
P. 155
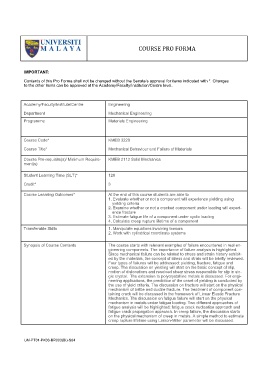
COURSE PRO FORMA
IMPORTANT:
Contents of this Pro Forma shall not be changed without the Senate’s approval for items indicated with *. Changes
to the other items can be approved at the Academy/Faculty/Institution/Centre level.
Academy/Faculty/Institute/Centre Engineering
Department Mechanical Engineering
Programme Materials Engineering
Course Code* KMEB 3220
Course Title* Mechanical Behaviour and Failure of Materials
Course Pre-requisite(s)/ Minimum Require- KMEB 2112 Solid Mechanics
ment(s)
Student Learning Time (SLT)* 120
Credit* 3
Course Learning Outcomes* At the end of this course students are able to
1. Evaluate whether or not a component will experience yielding using
yielding criteria
2. Examine whether or not a cracked component under loading will experi-
ence fracture
3. Estimate fatigue life of a component under cyclic loading
4. Calculate creep rupture lifetime of a component
Transferable Skills 1. Manipulate equations involving tensors
2. Work with cylindrical coordinate systems
Synopsis of Course Contents The course starts with relevant examples of failure encountered in real en-
gineering components. The importance of failure analysis is highlighted.
Since mechanical failure can be related to stress and strain history exhibit-
ed by the materials, the concept of stress and strain will be briefly reviewed.
Four types of failures will be addressed: yielding, fracture, fatigue and
creep. The discussion on yielding will start on the basic concept of slip,
motion of dislocations and resolved shear stress responsible for slip in sin-
gle crystal. The extension to polycrystalline metals is discussed. For engi-
neering applications, the prediction of the onset of yielding is conducted by
the use of yield criteria. The discussion on fracture will start on the physical
mechanism of brittle and ductile fracture. The treatment of component con-
taining crack will be discussed in the framework of Linear Elastic Fracture
Mechanics. The discussion on fatigue failure will start on the physical
mechanism in metals under fatigue loading. Two different approaches of
fatigue analysis will be highlighted: fatigue crack nucleation approach and
fatigue crack propagation approach. In creep failure, the discussion starts
on the physical mechanism of creep in metals. A simple method to estimate
creep rupture lifetime using Larson-Miller parameter will be discussed.
UM-PT01-PK03-BR003(BI)-S04