Page 11 - AEI Insights 2018 Vol 4 Issue 1
P. 11
AEI Insights, Vol 4, Issue 1, 2018
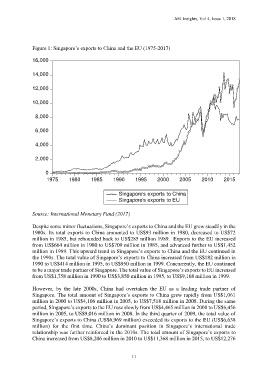
Figure 1: Singapore’s exports to China and the EU (1975-2017)
16,000
14,000
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
0
1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015
Singapore's exports to China
Singapore's exports to EU
Source: International Monetary Fund (2017)
Despite some minor fluctuations, Singapore’s exports to China and the EU grew steadily in the
1980s. Its total exports to China amounted to US$93 million in 1980, decreased to US$72
million in 1985, but rebounded back to US$285 million 1989. Exports to the EU increased
from US$664 million in 1980 to US$709 million in 1985, and advanced further to US$1,452
million in 1989. This upward trend in Singapore’s exports to China and the EU continued in
the 1990s. The total value of Singapore’s exports to China increased from US$182 million in
1990 to US$414 million in 1995, to US$950 million in 1999. Concurrently, the EU continued
to be a major trade partner of Singapore. The total value of Singapore’s exports to EU increased
from US$1,758 million in 1990 to US$3,850 million in 1995, to US$9,168 million in 1999.
However, by the late 2000s, China had overtaken the EU as a leading trade partner of
Singapore. The total amount of Singapore’s exports to China grew rapidly from US$1,061
million in 2000 to US$4,106 million in 2005, to US$7,518 million in 2008. During the same
period, Singapore’s exports to the EU rose slowly from US$4,465 million in 2000 to US$6,456
million in 2005, to US$9,016 million in 2008. In the third quarter of 2009, the total value of
Singapore’s exports to China (US$6,969 million) exceeded its exports to the EU (US$6,638
million) for the first time. China’s dominant position in Singapore’s international trade
relationship was further reinforced in the 2010s. The total amount of Singapore’s exports to
China increased from US$8,206 million in 2010 to US$11,368 million in 2015, to US$12,276
11