Page 66 - AEI Insights Vol. 7 2021
P. 66
AEI Insights, Vol 7, Issue 1, 2021
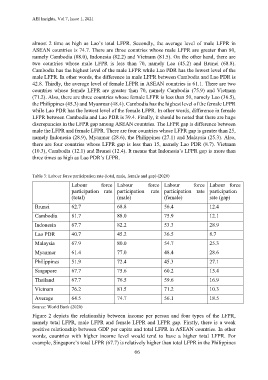
almost 2 time as high as Lao’s total LFPR. Secondly, the average level of male LFPR in
ASEAN countries is 74.7. There are three countries whose male LFPR are greater than 80,
namely Cambodia (88.0), Indonesia (82.2) and Vietnam (81.5). On the other hand, there are
two countries whose male LFPR is less than 70, namely Lao (45.2) and Brunei (68.8).
Cambodia has the highest level of the male LFPR while Lao PDR has the lowest level of the
male LFPR. In other words, the difference in male LFPR between Cambodia and Lao PDR is
42.8. Thirdly, the average level of female LFPR in ASEAN countries is 61.1. There are two
countries whose female LFPR are greater than 70, namely Cambodia (75.9) and Vietnam
(71.2). Also, there are three countries whose female LFPR is less than 50, namely Lao (36.5),
the Philippines (45.3) and Myanmar (48.4). Cambodia has the highest level of the female LFPR
while Lao PDR has the lowest level of the female LFPR. In other words, difference in female
LFPR between Cambodia and Lao PDR is 39.4. Finally, it should be noted that there are huge
discrepancies in the LFPR gap among ASEAN countries. The LFPR gap is difference between
male the LFPR and female LFPR. There are four countries whose LFPR gap is greater than 25,
namely Indonesia (28.9), Myanmar (28.6), the Philippines (27.1) and Malaysia (25.3). Also,
there are four countries whose LFPR gap is less than 15, namely Lao PDR (8.7). Vietnam
(10.3), Cambodia (12.1) and Brunei (12.4). It means that Indonesia’s LFPR gap is more than
three times as high as Lao PDR’s LFPR.
Table 3: Labour force participation rate (total, male, female and gap) (2020)
Labour force Labour force Labour force Labour force
participation rate participation rate participation rate participation
(total) (male) (female) rate (gap)
Brunei 62.7 68.8 56.4 12.4
Cambodia 81.7 88.0 75.9 12.1
Indonesia 67.7 82.2 53.3 28.9
Lao PDR 40.7 45.2 36.5 8.7
Malaysia 67.9 80.0 54.7 25.3
Myanmar 61.4 77.0 48.4 28.6
Philippines 51.9 72.4 45.3 27.1
Singapore 67.7 75.6 60.2 15.4
Thailand 67.7 76.5 59.6 16.9
Vietnam 76.2 81.5 71.2 10.3
Average 64.5 74.7 56.1 18.5
Source: World Bank (2020)
Figure 2 depicts the relationship between income per person and four types of the LFPR,
namely total LFPR, male LFPR and female LFPR and LFPR gap. Firstly, there is a weak
positive relationship between GDP per capita and total LFPR in ASEAN countries. In other
words, countries with higher income level would tend to have a higher total LFPR. For
example, Singapore’s total LFPR (67.7) is relatively higher than total LFPR in the Philippines
66