Page 67 - AEI Insights Vol. 7 2021
P. 67
Jingyi et al, 2021
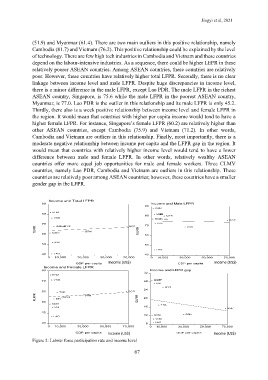
(51.9) and Myanmar (61.4). There are two main outliers in this positive relationship, namely
Cambodia (81.7) and Vietnam (76.2). This positive relationship could be explained by the level
of technology. There are few high tech industries in Cambodia and Vietnam and these countries
depend on the labour-intensive industries. As a sequence, there could be higher LEPR in these
relatively poorer ASEAN countries. Among ASEAN countries, these countries are relatively
poor. However, these countries have relatively higher total LFPR. Secondly, there is no clear
linkage between income level and male LFPR. Despite huge discrepancies in income level,
there is a minor difference in the male LFPR, except Lao PDR. The male LFPR in the richest
ASEAN country, Singapore, is 75.6 while the male LFPR in the poorest ASEAN country,
Myanmar, is 77.0. Lao PDR is the outlier in this relationship and its male LFPR is only 45.2.
Thirdly, there also is a week positive relationship between income level and female LFPR in
the region. It would mean that countries with higher per capita income would tend to have a
higher female LFPR. For instance, Singapore’s female LFPR (60.2) are relatively higher than
other ASEAN countries, except Cambodia (75.9) and Vietnam (71.2). In other words,
Cambodia and Vietnam are outliers in this relationship. Finally, most importantly, there is a
moderate negative relationship between income per capita and the LFPR gap in the region. It
would mean that countries with relatively higher income level would tend to have a lower
difference between male and female LFPR. In other words, relatively wealthy ASEAN
countries offer more equal job opportunities for male and female workers. Three CLMV
countries, namely Lao PDR, Cambodia and Vietnam are outliers in this relationship. These
countries are relatively poor among ASEAN countries; however, these countries have a smaller
gender gap in the LFPR.
Income and Total LFPR
90 Income and Male LFPR
90
KHM
80 KHM VNM
IDN
80 MYS
VNM
MMR THA
SGP
70 IDNTHA MYS SGP 70 PHL
TLFPR BRN MLFPR BRN
60 MMR 60
PHL
50 50
LAO
40 LAO 40
0 10,000 30,000 50,000 70,000 0 10,000 30,000 50,000 70,000
Income (US$) Income (US$)
GDP per capita GDP per capita
Income and Female LFPR
80 Income and LFPR gap
32
KHM
IDN
70 VNM 28 MMR
PHL
MYS
24
60 THA SGP
FLFPR IDN MYS BRN GLFPR 20
50
MMR THA
PHL 16 SGP
40
LAO 12 KHM BRN
VNM
30 8 LAO
0 10,000 30,000 50,000 70,000 0 10,000 30,000 50,000 70,000
GDP per capita Income (US$) GDP per capita Income (US$)
Figure 2: Labour force participation rate and income level
67