Page 71 - ASEAN-EU Dialogue 2018: Regional and Inter-Regional Economic Cooperation: Identifying Priorities for ASEAN and the EU
P. 71
20
16
12
8
4
0
1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015
DENMARK FINLAND
NORWAY SWEDEN
Source: World Bank (2018)
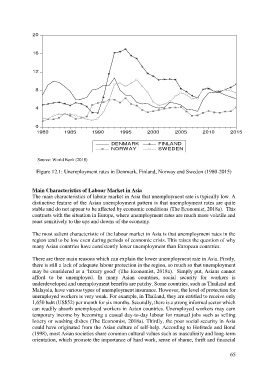
Figure 12.1: Unemployment rates in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden (1980-2015)
Main Characteristics of Labour Market in Asia
The main characteristics of labour market in Asia that unemployment rate is typically low. A
distinctive feature of the Asian unemployment pattern is that unemployment rates are quite
stable and do not appear to be affected by economic conditions (The Economist, 2018a). This
contrasts with the situation in Europe, where unemployment rates are much more volatile and
react sensitively to the ups and downs of the economy.
The most salient characteristic of the labour market in Asia is that unemployment rates in the
region tend to be low even during periods of economic crisis. This raises the question of why
many Asian countries have consistently lower unemployment than European countries.
There are three main reasons which can explain the lower unemployment rate in Asia. Firstly,
there is still a lack of adequate labour protection in the region, so much so that unemployment
may be considered as a ‘luxury good’ (The Economist, 2018a). Simply put, Asians cannot
afford to be unemployed. In many Asian countries, social security for workers is
underdeveloped and unemployment benefits are patchy. Some countries, such as Thailand and
Malaysia, have various types of unemployment insurance. However, the level of protection for
unemployed workers is very weak. For example, in Thailand, they are entitled to receive only
1,650 baht (US$52) per month for six months. Secondly, there is a strong informal sector which
can readily absorb unemployed workers in Asian countries. Unemployed workers may earn
temporary income by becoming a casual day-to-day labour for manual jobs such as selling
lottery or washing dishes (The Economist, 2018a). Thirdly, the poor social security in Asia
could have originated from the Asian culture of self-help. According to Hofstede and Bond
(1998), most Asian societies share common cultural values such as masculinity and long-term
orientation, which promote the importance of hard work, sense of shame, thrift and financial
65