Page 71 - AEI Insights 2020 - Vol. 6, Issue 1
P. 71
Bajrektarevic, 2020b
• link between environmental crimes and corruption is facilitated by a legal approach is
formalistic = focused on legislation that would punish environmental crimes, regardless
of the actual damage caused, on the ground of abstract danger
• lack of common definition - no internationally recognized definition on environmental
crime – only an often used common understanding
• international legal mechanisms are need to be established and enforced at national level
to implement international environmental law
• illegal activities pose a challenge on law enforcement and implementation (including
MEAs)
• lack of understanding and approaches between and among States – a relatively new
category to combat transnational crimes - internationally coordinated efforts and a law
enforcement cooperation are needed
• lack of funding to fight crime knowledge gap between environmental crimes and
corruption
• actors that are combating environmental crimes are usually under-resourced in contrast
with the criminal environment (which have the financial means)
• significant availability of money by committing these crimes at the expense of the
environment
• best source of criminal intelligence is from INTERPOL
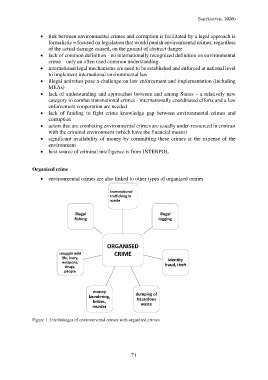
Organized crime
• environmental crimes are also linked to other types of organized crimes
transnational
trafficking in
waste
illegal illegal
fishing logging
ORGANISED
smuggle wild CRIME
life, ivory, identity
weapons,
drugs, fraud, theft
people
money
laundering, dumping of
bribes, hazardous
murder waste
Figure 1: Interlinkages of environmental crimes with organized crimes
71