Page 92 -
P. 92
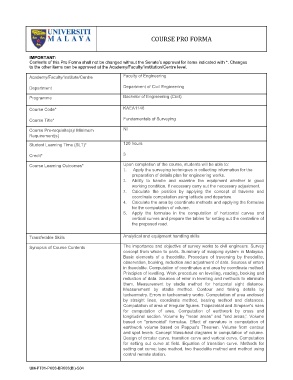
COURSE PRO FORMA
IMPORTANT:
Contents of this Pro Forma shall not be changed without the Senate’s approval for items indicated with *. Changes
to the other items can be approved at the Academy/Faculty/Institution/Centre level.
Academy/Faculty/Institute/Centre Faculty of Engineering
Department Department of Civil Engineering
Programme Bachelor of Engineering (Civil)
Course Code* KAEA1146
Course Title* Fundamentals of Surveying
Course Pre-requisite(s)/ Minimum Nil
Requirement(s)
Student Learning Time (SLT)* 120 hours
Credit* 3
Course Learning Outcomes* Upon completion of the course, students will be able to:
1. Apply the surveying techniques in collecting information for the
preparation of details plan for engineering works.
2. Ability to handle and examine the equipment whether in good
working condition. If necessary carry out the necessary adjustment.
3. Calculate the position by applying the concept of traverse and
coordinate computation using latitude and departure.
4. Calculate the area by coordinate methods and applying the formulae
for the computation of volume.
5. Apply the formulae in the computation of horizontal curves and
vertical curves and prepare the tables for setting out the centreline of
the proposed road.
Transferable Skills Analytical and equipment handling skills
Synopsis of Course Contents The importance and objective of survey works to civil engineers. Survey
concept from whole to parts. Summary of mapping system in Malaysia.
Basic elements of a theodolite. Procedure of traversing by theodolite,
observation, booking, reduction and adjustment of data. Sources of errors
in theodolite. Computation of coordinates and area by coordinate method.
Principles of levelling. Work procedure on levelling, reading, booking and
reduction of data. Sources of error in levelling and methods to eliminate
them. Measurement by stadia method for horizontal sight distance.
Measurement by stadia method. Contour and taking details by
tacheometry. Errors in tacheometry works. Computation of area enclosed
by straight lines, coordinate method, bearing method and distances.
Computation of area of irregular figures. Trapezoidal and Simpson's rules
for computation of area. Computation of earthwork by cross and
longitudinal section. Volume by "mean areas" and "end areas,'. Volume
based on "prismoidal" formulae. Effect of curvature in computation of
earthwork volume based on Pappus's Theorem. Volume from contour
and spot levels. Concept Mass-haul diagrams in computation of volume.
Design of circular curve, transition curve and vertical curve. Computation
for setting out curve at field. Equation of transition curve. Methods for
setting out curve; tape method, two theodolite method and method using
control remote station.
UM-PT01-PK03-BR003(BI)-S04